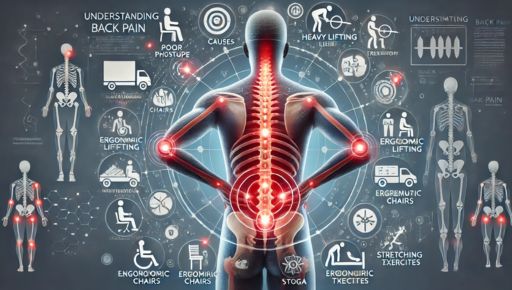
Back pain is one of the most common health problems people face worldwide. It can range from a mild discomfort to a debilitating condition that interferes with daily activities. Whether it’s caused by poor posture, a sudden injury, or a more serious medical condition, understanding the underlying causes of back pain, exploring various treatment options, and learning how to prevent it can significantly improve your quality of life.
What Is Back Pain?
Back pain refers to any discomfort, soreness, or injury that affects the spine, muscles, ligaments, or nerves in the back. The spine is made up of vertebrae, discs, and nerves, and the surrounding muscles and ligaments. When any of these components are damaged or inflamed, it can result in pain. Back pain is categorized into acute (short-term) or chronic (long-term), and it can vary in intensity from a dull ache to a sharp, shooting pain.
Common Causes of Back Pain
Understanding the causes of back pain is crucial to finding the right treatment. The most common causes include:
1. Poor Posture
One of the leading causes of back pain is poor posture. Sitting or standing in an incorrect position for extended periods can strain the muscles and ligaments of the back. Over time, this strain leads to discomfort and pain. People who sit at desks for long hours or hunch over their phones are particularly prone to developing back pain.
2. Muscle Strain or Ligament Sprain
Heavy lifting, twisting movements, or sudden jerks can cause muscle strains or ligament sprains. These injuries are often the result of improper lifting techniques or overexertion, and they typically lead to localized pain in the lower back.
3. Herniated Discs
A herniated disc, also known as a slipped or ruptured disc, occurs when the soft tissue inside the spine’s discs bulges out. This can press on nearby nerves, causing pain, numbness, or tingling sensations in the back and legs. Herniated discs are most common in the lower back.
4. Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease, can lead to back pain as the cartilage in the spine wears away. This condition causes the bones in the spine to rub together, leading to pain, stiffness, and inflammation. Osteoarthritis is more common in older adults but can affect younger people as well.
5. Sciatica
Sciatica refers to pain that radiates along the sciatic nerve, which runs from the lower back down to the legs. Sciatica is usually caused by a herniated disc or spinal stenosis that compresses the nerve, leading to sharp, shooting pain, often on one side of the body.
6. Spinal Stenosis
Spinal stenosis is the narrowing of the spaces within the spine, which puts pressure on the spinal cord and nerves. This can lead to symptoms like back pain, numbness, and weakness, especially in the legs.
7. Scoliosis
Scoliosis is an abnormal curvature of the spine, which can lead to back pain, particularly if the curve is severe. While scoliosis often develops during childhood or adolescence, it can also be diagnosed in adulthood.
Treatment Options for Back Pain
Treating back pain depends on its underlying cause and severity. In most cases, back pain can be managed with conservative treatments, but more severe cases may require medical intervention.
1. Rest and Activity Modification
For acute back pain, the first step is often rest. Avoiding activities that exacerbate the pain can help the muscles and ligaments heal. However, prolonged bed rest is not recommended, as it can lead to stiffness and muscle weakness. Gentle movement and stretching can help keep the back muscles flexible.
2. Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is one of the most effective treatments for back pain. A physical therapist can guide patients through exercises that strengthen the back muscles, improve posture, and increase flexibility. These exercises help reduce the likelihood of future back pain episodes.
3. Medications
Over-the-counter medications, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can provide relief for mild back pain. For more severe cases, doctors may prescribe muscle relaxants or stronger pain medications. In some instances, steroid injections may be used to reduce inflammation and provide pain relief.
4. Heat and Cold Therapy
Applying heat or cold to the affected area can help reduce inflammation and ease muscle tension. Cold packs are best for acute injuries, while heat pads are effective for chronic pain and muscle stiffness.
5. Surgery
In rare cases, surgery may be necessary to treat severe back pain caused by conditions like herniated discs, spinal stenosis, or scoliosis. Surgical options include discectomy (removal of part of a herniated disc) or spinal fusion (joining two vertebrae together to reduce movement). Surgery is generally only considered when other treatments have failed.
Prevention of Back Pain
While some causes of back pain are unavoidable, there are several steps you can take to reduce the risk and prevent future episodes.
1. Maintain Good Posture
Practicing good posture is essential for preventing back pain. Ensure that your spine is aligned whether you’re sitting, standing, or sleeping. When sitting, use a chair with proper back support, and avoid slouching. When standing, keep your weight evenly distributed on both feet.
2. Exercise Regularly
Regular exercise is one of the best ways to prevent back pain. Focus on exercises that strengthen your core, improve flexibility, and promote good posture. Activities like yoga, swimming, and walking can help keep your back muscles strong and flexible.
3. Use Proper Lifting Techniques
When lifting heavy objects, use your legs to lift, not your back. Bend your knees, keep your back straight, and avoid twisting your body. If the object is too heavy, ask for help or use a lifting device.
4. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Carrying excess weight, especially around the abdomen, can strain the back. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can help alleviate stress on the spine and reduce the risk of developing back pain.
5. Sleep in a Supportive Position
Your sleeping position can affect your back. Use a mattress that provides adequate support and pillows that help maintain the natural curve of your spine. Sleeping on your back with a pillow under your knees or on your side with a pillow between your legs can help prevent back pain.
When to Seek Medical Help
In most cases, back pain improves with self-care and conservative treatments. However, you should consult a doctor if you experience:
- Persistent pain that lasts for more than a few weeks
- Severe pain that interferes with daily activities
- Numbness, tingling, or weakness in your legs
- Pain after a fall or injury
- Difficulty controlling bladder or bowel movements
Conclusion
Back pain is a common yet complex issue that affects people of all ages and lifestyles. Understanding the causes, treatments, and prevention methods can help you manage back pain and prevent it from recurring. Whether through lifestyle changes, physical therapy, or medication, many options are available to reduce pain and improve your quality of life. If your back pain persists, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider to ensure that you receive the right care and treatment.